In micro-economics we noted that the demand curve of a normal goods say X is downward sloping largely due to. Here is an explanation of how Giffen goods can occur including examples from history.
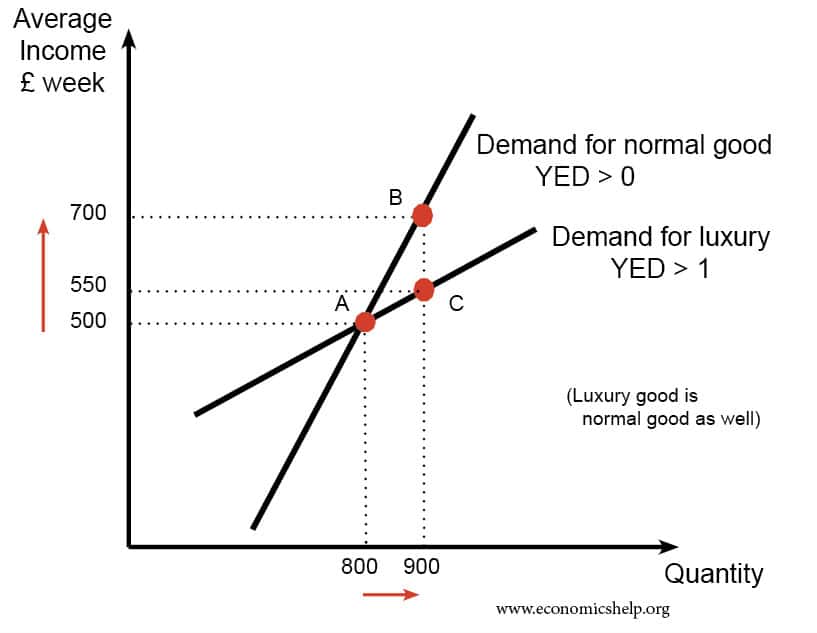
Different Types Of Goods Inferior Normal Luxury Economics Help
Derivation of Demand curve from PCC Normal Goods.
. Downward sloping only if the substitution effect is larger than the income effect. You also know that the point 120000 smart phones 0 per smart phone sits on the new market demand curve. If a good is a.
A shift in a demand curve occurs when a goods quantity demanded changes even though the price remains the same. This implies that the two demand curves have the same slope. This demand curve captures the specific one-to-one law of demand relation between demand price and quantity demanded.
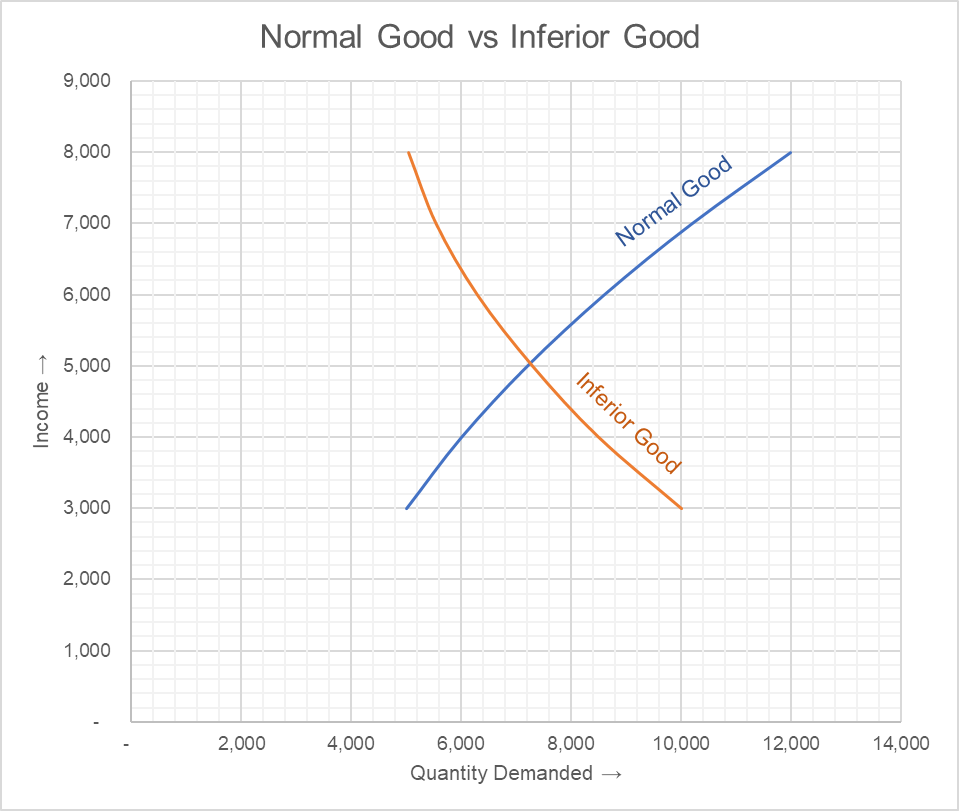
Derivation of the Consumers. The upper panel of Figure1 shows price effect where good X is a normal good. The demand curve for normal goods moves in the opposite direction as the curve for inferior goods.
FIGURE1 Derivation of the Demand Curve. A change in income causes a positive change in demand for normal goods whereas a negative change occurs in the case of inferior goods. In fig X-axis shows the quantity of Maggi demanded whereas Y-axis shows the quantity of the other commodity.
For example you may be willing to buy 10 apples at 1. If the grocery store drops the price to 075 then that demand curve movement means you might buy 15 apples instead. The line will be lower on the left and move higher as it moves right across.
A consumer is able to purchase a normal good and has a demand curve D1 which provides the relationship between price and quantity given his. Effect on Demand Curve with change in Income. The consumer buys OX units of good X.
For normal goods the demand curve is. Such a curve is shown in Figure 257 The Demand Curve. Giffen goods are goods that have upward-sloping demand curves.
The demand curve is downward sloping showing inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded as good X is a normal good. Normal goods in economics are the goods that consumers demand more when their income rises and the same demand fall-off when their income is declining. Buyers income is assumed to remain constant with the.
When income increases the demand curve for normal goods shifts outward as more will be demanded at all prices while the demand curve for inferior goods shifts inward due to the. Factors causing a shift in the demand curve. Size of the.

How Does The Demand Curve Of Normal Goods Change When The Income Of The Buyer Changes Homework Study Com
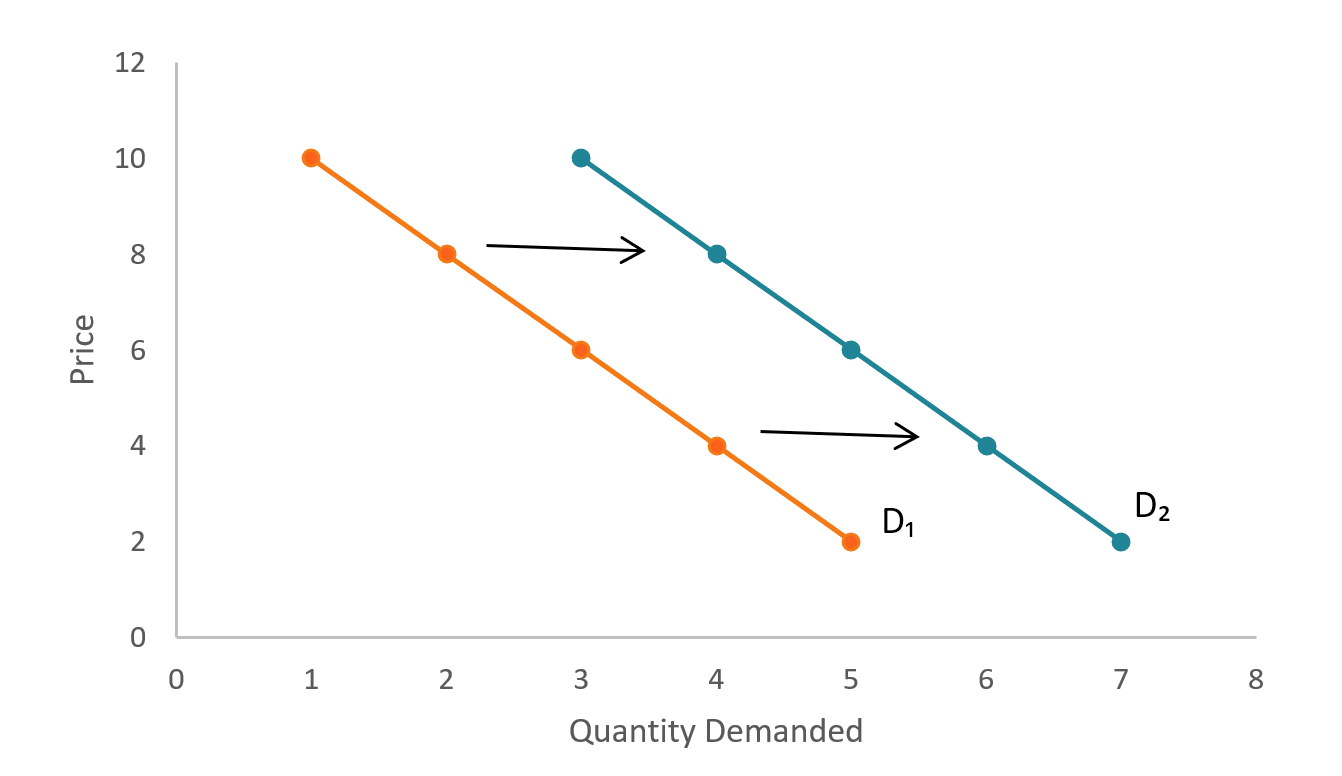
Normal Goods Definition Graphical Representation And Examples

0 Comments